Pledges of insurance policies
| Pledges possible? (YES/NO) | Existing types of pledge | Functioning of the pledges | |
| Luxembourg | YES |
1. Assignment of debt (Article 1275 et seq. of the Luxembourg Civil Code). 2. Pledge (Article 116 et seq. of the amended Luxembourg Law of 27 July 1997 on Insurance Policies, and Articles 2071 et seq. of the Luxembourg Civil Code). 3. Assignment of rights (Articles 118 et seq. of the Amended Law of 27 July 1997 on Insurance Policies). |
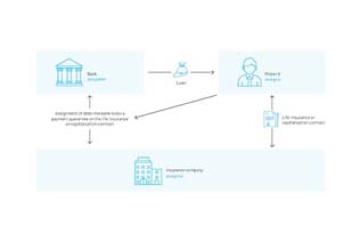
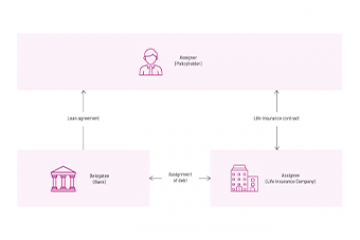
1. Assignment of debt: a legal transaction by which one person (the assignee) undertakes to comply with the instructions of another person (the assignor) towards a third person (the delegatee). 2. Pledge: the rights arising under a policy may only be pledged by the policyholder. This type of security consists in the subscriber delivering the policy to the creditor as guarantee for his debt. The policy may only be pledged by an additional clause signed by the policyholder or debtor, the pledgor, and the insurer. 3. Assignment of rights: the rights arising under an insurance policy may be assigned, in whole or in part, by the policyholder. Total or partial assignment may only be made by means of a tripartite amendment between the insurance company, the policyholder and the secured creditor. There are three types of assignment: transfers of full ownership, transfers up to the sums due, and transfers of all the rights arising under a policy. |
| France | YES |
1. Assignment of debt (governed by Articles 1336 et seq. of the French Civil Code). 2. Pledge (Article L132-10 of the French Insurance Code and Articles 2355 et seq. of the French Civil Code). |
1. Assignment of debt: a legal transaction by which one person (the assignee) undertakes to comply with the instructions of another person (the assignor) towards a third person (the delegatee). 2. Pledge: the assignment, as security for a debt, of an intangible asset or a set of intangible assets, present or future. An insurance policy may be pledged either by amendment or by deed subject to the formalities required by Articles 2355 to 2366 of the Civil Code. |
| Belgium | YES |
1. Assignment of claim 2. Pledge (= Charge) 3. Assignment of rights |
1. Assignment of debt: for a policyholder: right to claim (= debt of the insurance company) - tripartite agreement. Belgian law does not provide for any formalities. 2. Pledge: Art. 181. The rights resulting from the insurance policy may be pledged;only by the policyholder, to the exclusion of his spouse and his creditors. If accepted, the pledge is subject to the consent of the beneficiary. 3. Assignment of rights: |
| Italy | YES |
In Italian law, this is called a “pegno". This is a type of security similar to a “charge" (Articles 2787 and 2800 of the Italian Civil Code). |
The bank and the policyholder sign a pledge and notify the insurance company. The company makes an annex to the contract, notifies and delivers it to the client and to the bank. |
| Germany | YES |
1. Pledge 2. Assignment of Rights |
1. Pledge: The policyholder (or “pledgor") delivers the policy, which is a bearer instrument, to the creditor (or “pledgee"). 2. Assignment of Rights: The policyholder (or “assignor") assigns his policy rights to a third party, usually the creditor (or “assignee"). |
| Poland | YES |
Pledge |
The agreement setting up the pledge should be made in writing with a certified date, even though it is not necessary to comply with this formality when transferring a right. For a pledge to be set up, the pledgor (policy holder) must give written notification to the debtor of the receivable (the insurance company). |
| UK | YES |
Pledge |
In order that an assignment of a life insurance policy to a lending institution may be recognised, the following conditions must be met: |
| Spain | YES |
In Spanish law, this is called a "Pignoración de la póliza". This is a type of security similar to a "pledge". |
Where the pledge is intended to constitute a privilege over the insurance policy, and therefore, the mere possibility of transfer if the primary obligation is not honoured... |
| The Netherlands | YES |
1. A ‘pandrecht' is based on Articles 3:236 and 3:237 of the Burgerlijk Wetboek (the Dutch Civil Code). A pledge of rights is a document which must be registered or established by a notary. |
A right of pledge may be established over all transferable goods. Therefore, a unit-linked insurance policy may be pledged. If there is a ‘pandrecht’ over an insurance contract, permission from the pledgee is required in order to make changes to the policy. The pledge is an agreement between the two parties (for example client and bank). The insurance company must be notified. |
| Portugal | YES |
1. Assignment of claim (a Luxembourg mechanism, not provided for in Portuguese law but often used in practice). 2. Pledge (penhor - Article 666 of the Portugese Civil Code. 3. Assignment of a right (an assignment of or encumbrance on the rights under Art. 196 of the Portuguese Insurance Law and Art. 577 of the Portuguese Civil Code). |
1. Assignment of debt: for a policyholder, this means his right to claim (= a debt of the insurance company) - tripartite agreement. 2. A pledge entitles the creditor to payment of his claim, plus interest if any, with preference over other creditors, by applying the value of a certain movable asset, belonging to the debtor or to a third party. The pledge is an agreement between the policyholder and the bank, so the insurance company only has to be notified. 3. The right to surrender or any other right of the policyholder, the insured or the beneficiary, may be assigned or charged in accordance with the general rules, and must be notified to the life insurance company. |
| Finland | YES | Under Finnish law, the policyholder is entitled to assign and pledge the right held under a life insurance policy (Art. 51 of the Insurance Policies Law no. 543 of 28 June 1994). |
The policyholder and the pledgee sign a pledge and must notify the life insurance company. The company makes an annex to the contract, notifies and sends them to the policyholder and the pledgee. |
| Sweden | YES | The policyholder has the right to pledge his life insurance policy (Insurance Policies Act 2005: 104, Chapter 3 - Section 14 - Article 9). | The policyholder and the pledgee sign a Pledge and must notify the insurance company. The company makes an annex to the contract, notifies and sends them to the policyholder and the pledgee. |
| Monaco | YES |
1. Assignment of claim 2. Charge or Pledge |
1. Assignment of debt: legal transaction by which one person (the assignee) undertakes to comply with the instructions of another person (the assignor) towards a third person (the delegatee). It is triangular transaction consisting in an act made by the assignor, a commitment by the assignee, and an acceptance by the delegatee (or by other parties, such as the insured, if he is not the same person as the subscriber). 2. Charge or Pledge: the assignment, as security for an obligation, of an intangible personal asset or a group of intangible personal assets, present or future. |
Depending on the policyholder's country of residence, the type of guarantee that can be made on a life insurance contract will be different. Indeed, one can speak of assigments of debt, collateral or assignment of rights in Luxembourg, whereas pledging will be more common in France, Italy and Spain. The possibilities offered for pledging a life insurance contract depend on the policyholder's country of residence.